To ensure your application runs smoothly on your local machine and is accessible online, you’ll need to connect a domain or subdomain to your shared hosting. For detailed steps on how to connect a domain to your hosting, you can find resources online or check with your hosting provider.
Although the examples provided use NPM (Node Package Manager) to run commands, you’re not limited to it. You can use other JavaScript environments for your projects if preferred. For more details, visit the respective websites for the tools you’re using.
Note: It’s important to run commands like npm run build on your own computer. The server might have a different setup than your local environment, so an app that works on your computer may not build correctly on a different system.
Deploying React.js (Vite.js) and React Native apps
Deploying a Next.js app
Deploying React.js (Vite.js) and React Native apps
1. Create a deployment-ready build or dist folder
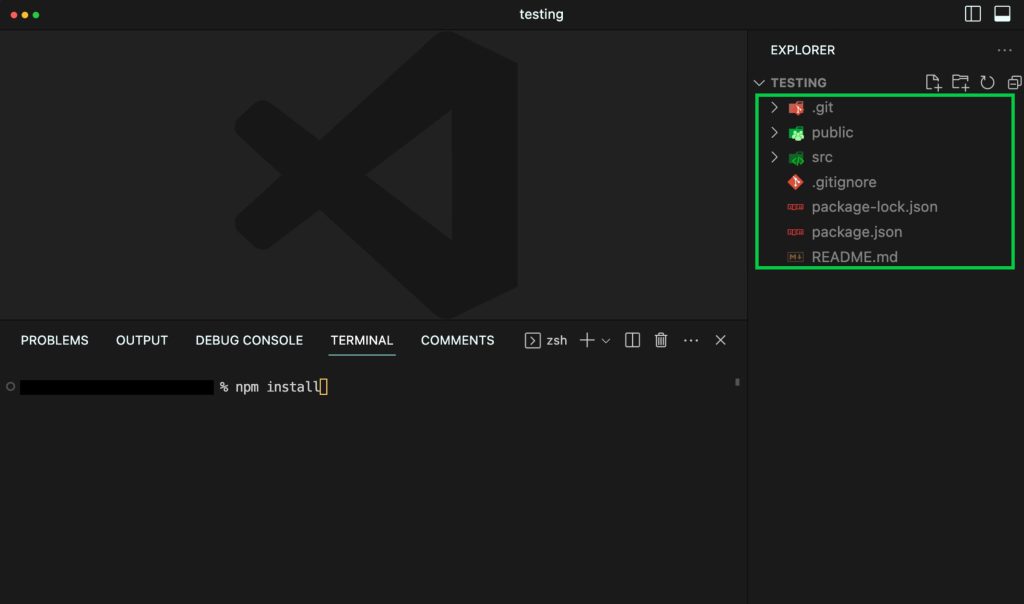
Open the app’s content in your local machine’s code editor (IDE). In the example, Visual Studio Code is used. Make sure that node modules are installed. If not, you can install them by running:
npm install
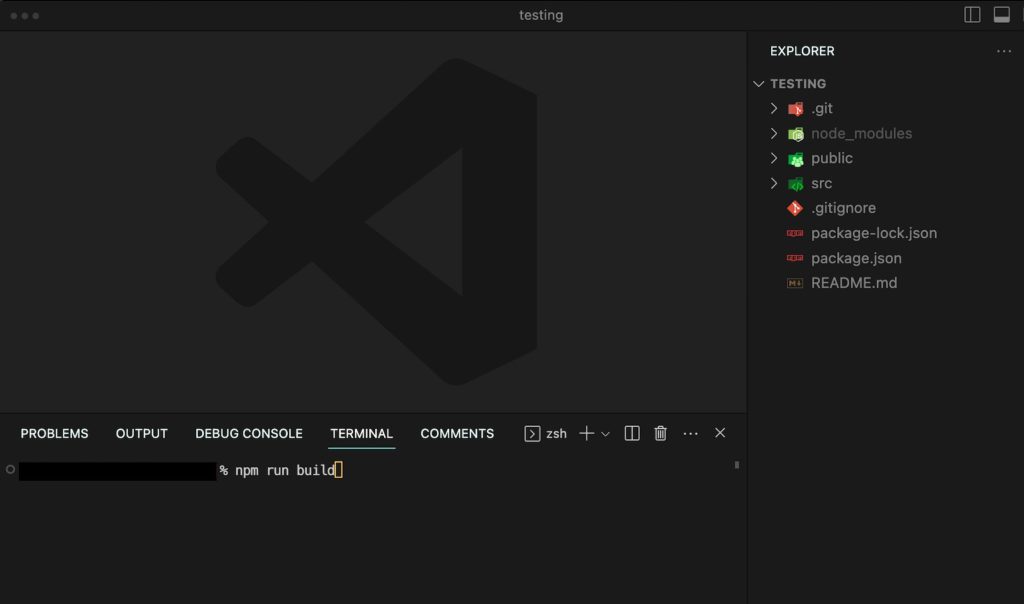
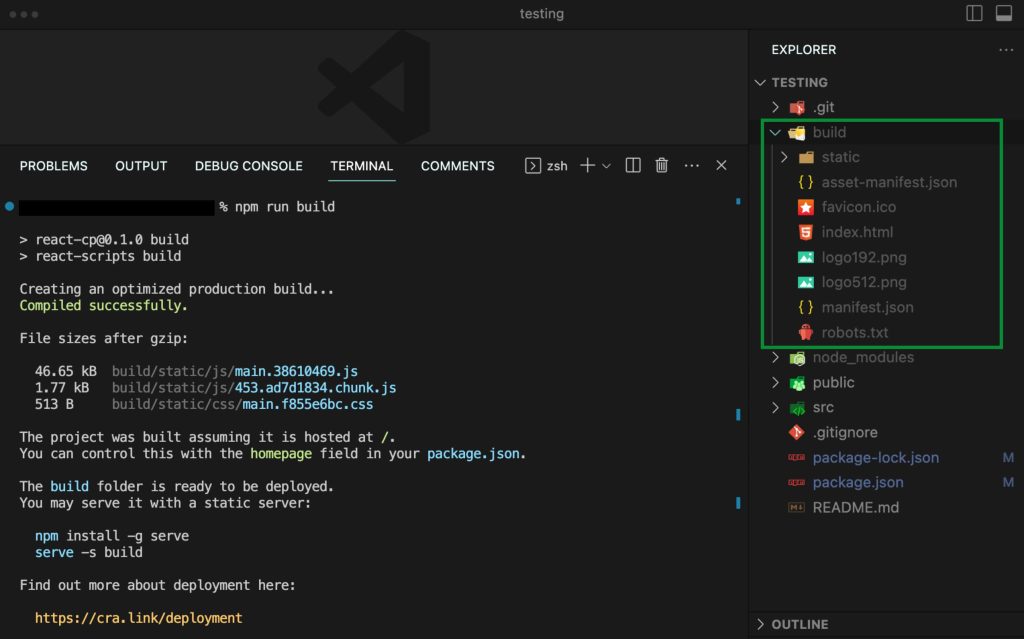
Once the node modules are present, you can build your React.js (Vite.js) app by running:
npm run build
React Native is a framework for building mobile apps that work on both Android and iOS. You can also use it to add extra packages before setting up the app for use on a website. Learn more about it online.
developing websites with React Native (Expo).
Also, ensure that you have the latest version of NPM, which can be installed with the command npm install -g npm and check that Expo is installed. You can install Expo with npm install expo-cli –global. Using Yarn, you can install Yarn by running npm install –global yarn, then yarn add expo.
For React Native run the following commands:
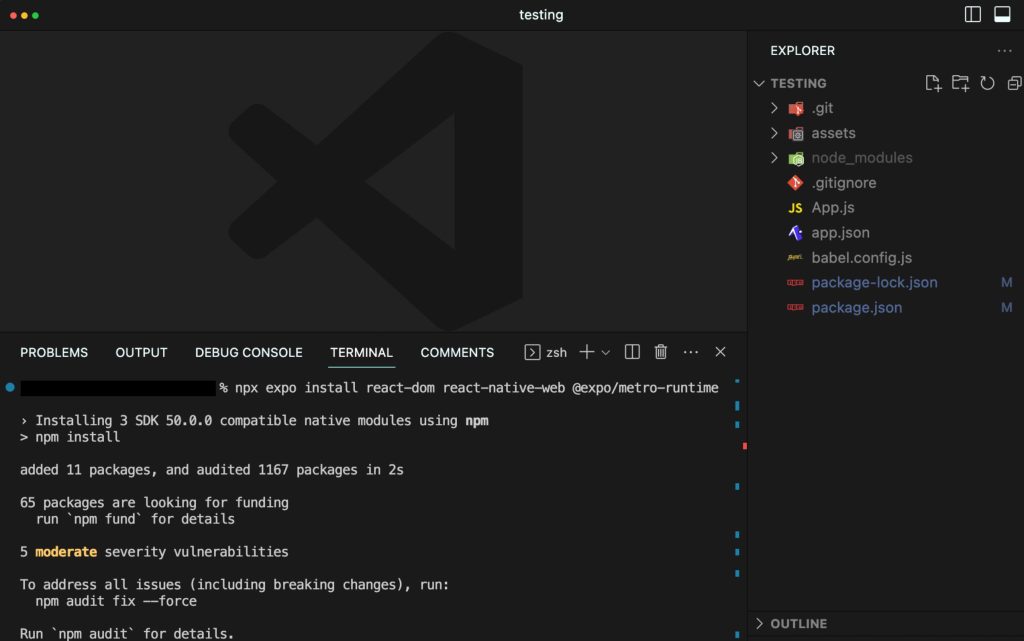
npx expo install react-dom react-native-web @expo/metro-runtime
npx expo export –platform web
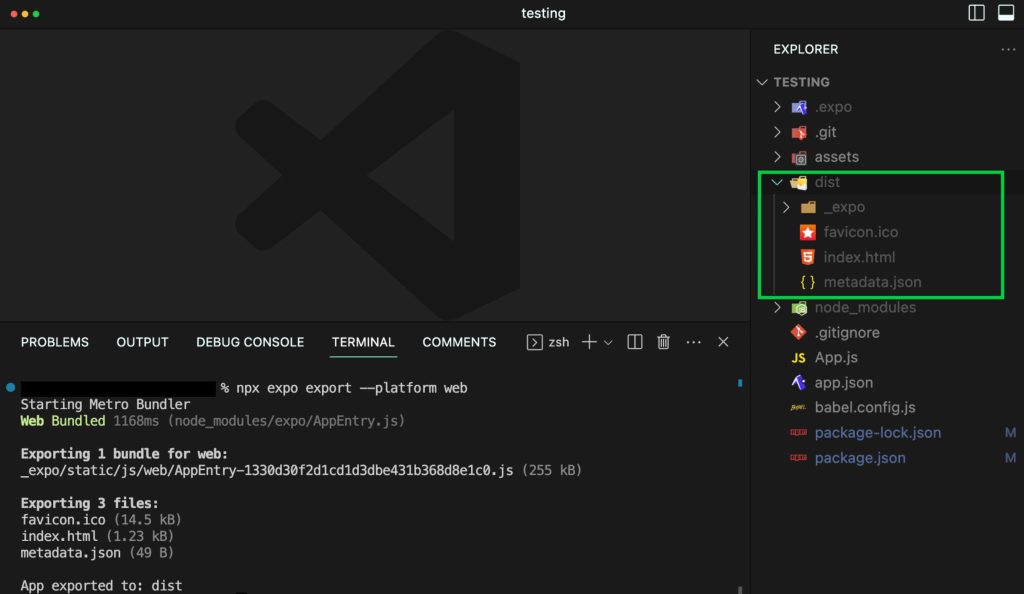
When this is finished, the build folder — or the dist folder for React.js apps built with Vite.js and React Native apps, will be created on your local machine. Then you need to compress the build or dist folder using any archiver. The compressed file should be deployed to your hosting.
2. Upload the build or dist folder to your cPanel
Learn more about how to upload your website files via File Manager, FTP, or SSH.
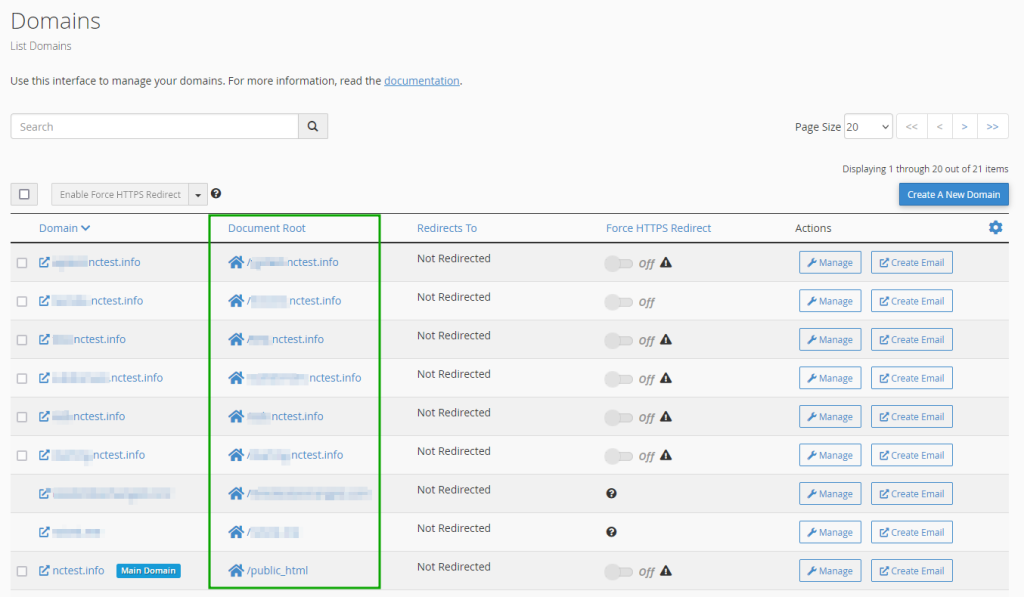
After importing the compressed folder, extract the content, and move all files and folders to the website’s root folder (found in the Domains menu). For the main domain, use the public_html folder, and for addon domains and subdomains, use the root folder.
For uploading files via File Manager:
- Log into your cPanel.
- Navigate to Domains >> Domains menu
- Go to your website’s root directory.
- Select Upload from the top menu.
- Choose the compressed build or dist file from your local machine and start the upload.
- When the upload is complete, go back to the website directory.
- Right-click on the uploaded file and choose Extract:
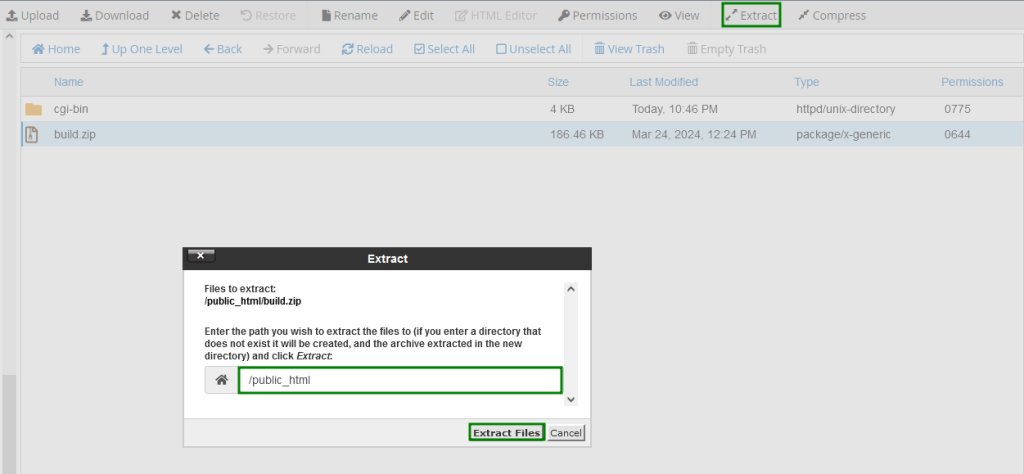
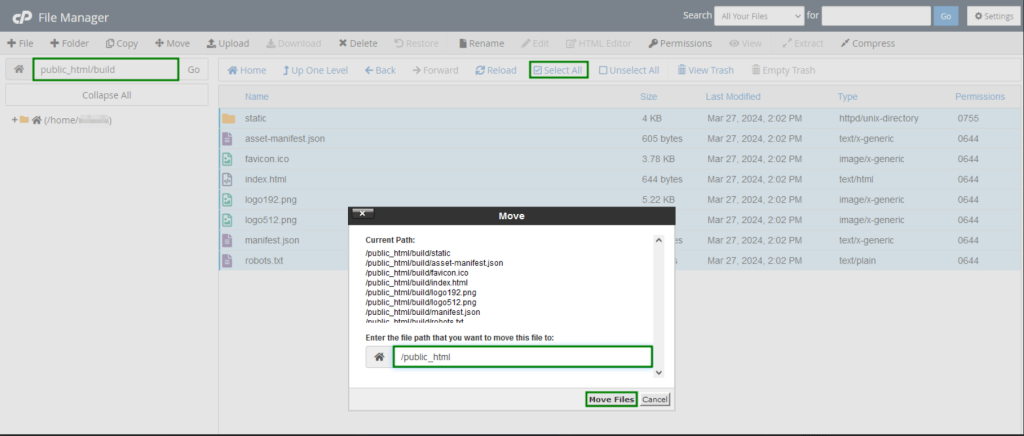
After the files are extracted, you should see a build or dist directory. Open this directory, select all the files and folders, then move them to the website directory.Now that the build or dist directory is empty, you can delete it.
3. Create the .htaccess file
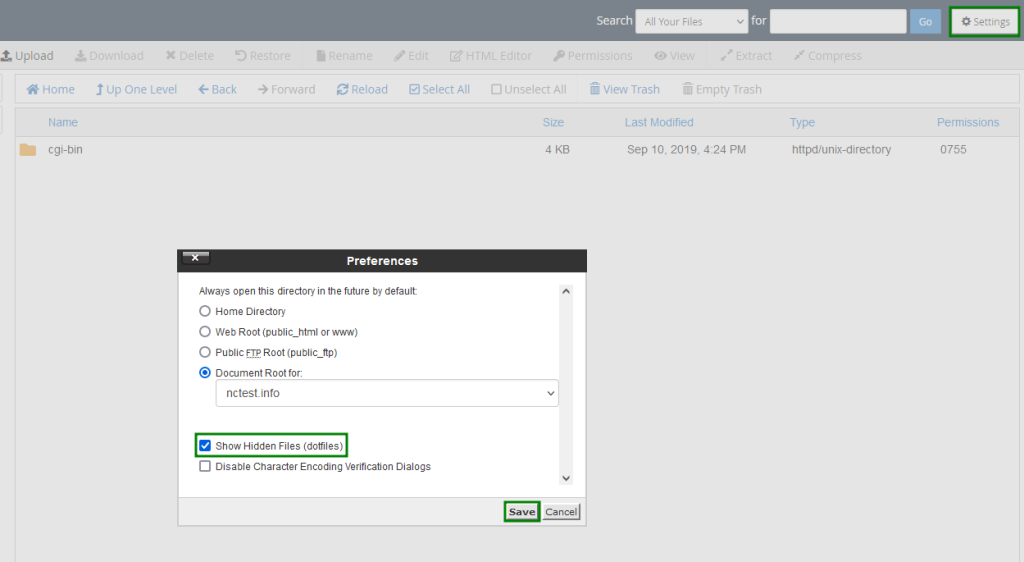
- Make sure the option to “Show Hidden Files (dotfiles)” is turned on in the Settings menu.
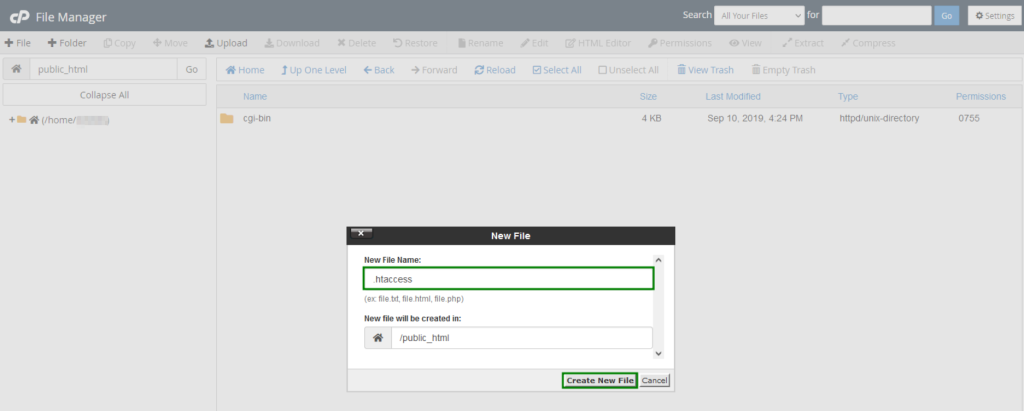
- Click the “+File” button, and a pop-up box will open. Type “.htaccess” as the file name and then click “Create New File.”
Select the .htaccess file and choose Edit:
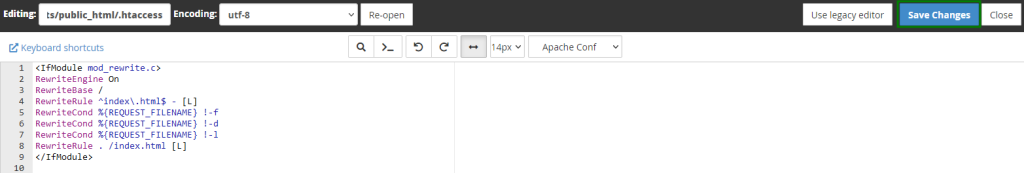
- Enter the following rule:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.html$ – [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-l
RewriteRule . /index.html [L] - Select Save Changes then close the editor:
Find this video guide on how to access and edit the .htaccess file.
Open a new tab in your web browser and enter your website URL. Now you should see your React.js app running.
Congratulations! You have deployed your React.js App to cPanel shared hosting.
NOTE: Compatible Node.js and Next.js versions are shown on the Next.js website:
Next.js 14: Node.js 18.17
Next.js 13: Node.js 16.14.0
Next.js 12: Node.js 12.22.0
To prepare a Next.js app for deployment, you need to create a custom Next.js server (server.js), modify the package.json file, and build the app.
1. Create a custom Next.js server (server.js)
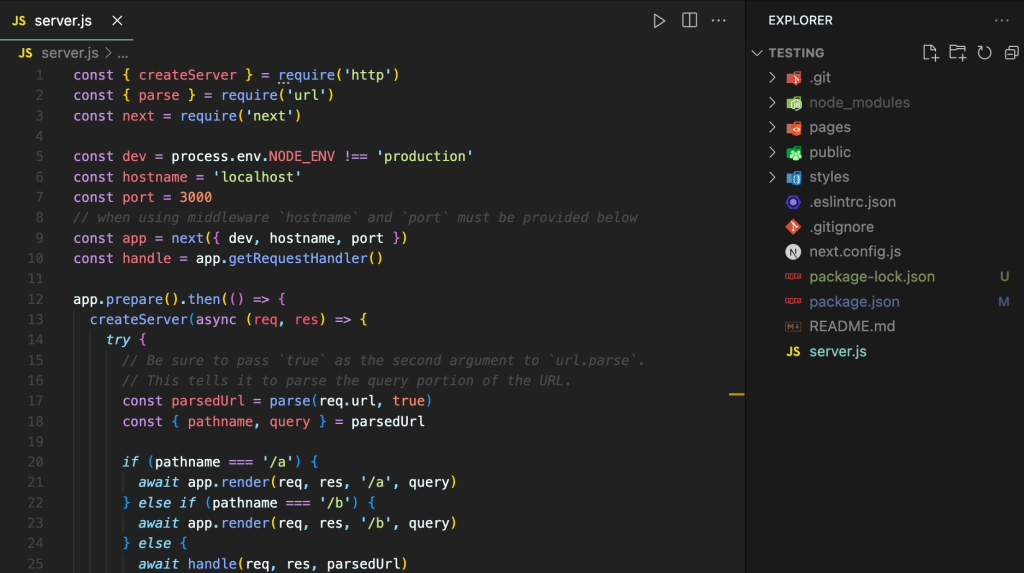
Create a server.js file in the root directory, you can check the Next.js guide for what’s needed. Add this code to the file:
const { createServer } = require(‘http’)
const { parse } = require(‘url’)
const next = require(‘next’)
const dev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’
const hostname = ‘localhost’
const port = 3000
// when using middleware `hostname` and `port` must be provided below
const app = next({ dev, hostname, port })
const handle = app.getRequestHandler()
app.prepare().then(() => {
createServer(async (req, res) => {
try {
// Be sure to pass true as the second argument to url.parse.
// This tells it to parse the query portion of the URL.
const parsedUrl = parse(req.url, true)
const { pathname, query } = parsedUrl
if (pathname === ‘/a’) {
await app.render(req, res, ‘/a’, query)
} else if (pathname === ‘/b’) {
await app.render(req, res, ‘/b’, query)
} else {
await handle(req, res, parsedUrl)
}
} catch (err) {
console.error(‘Error occurred handling’, req.url, err)
res.statusCode = 500
res.end(‘internal server error’)
}
})
.once(‘error’, (err) => {
console.error(err)
process.exit(1)
})
.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`> Ready on http://${hostname}:${port}`)
})
})
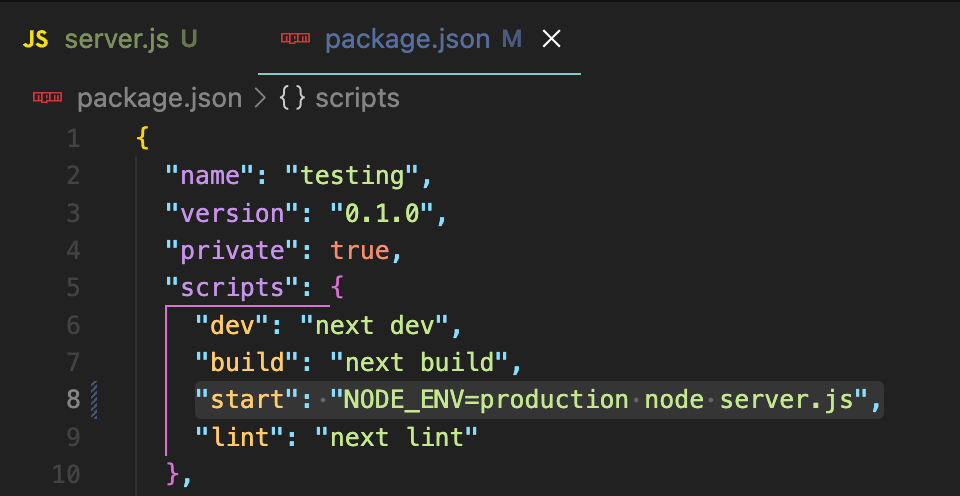
. Modify the package.json file
Modify the package.json file to set the environment to production on the start script and run the server.js file you created in the project root directory. Here you’ve replaced the default Next start server script with our own custom server.
{
“scripts”: {
“start”: “NODE_ENV=production node server.js”,
}
}
ake sure you install the required dependencies by running npm install in your terminal.
3. Build a Next.js application
To build a Next.js application:
- Open your terminal and navigate to your project directory.
- Run the build command:
npm run build
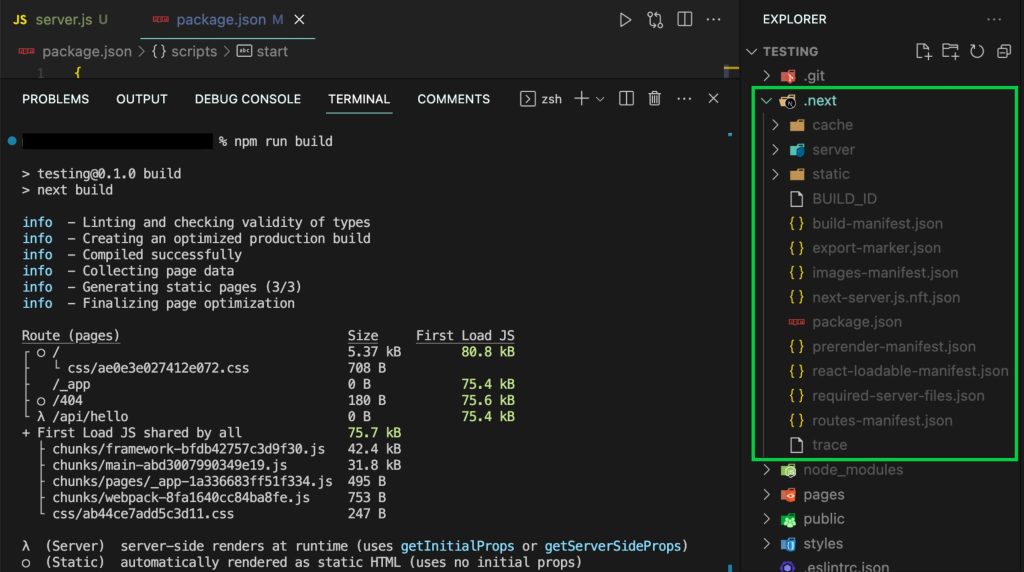
Make sure there are no errors while building the project. If you find any, fix them before continuing.
4. Prepare Files for Deployment
- Open the file manager and locate your Next.js project files.
- Enable visibility for any hidden files.
- Exclude the following folders/files:
- node_modules;
- .git;
- README.md;
- .gitignore.
- Select all remaining files and folders.
- Create a ZIP archive of the selected files:
It’s important to leave out the node_modules folder because it’s usually large and not needed for deployment. The required modules will be installed on the server later.
5. Upload the archive file to your cPanel on shared hosting.
Learn how to upload your website files via File Manager, FTP, or SSH.
NOTE: The public_html folder of the main domain cannot be used to configure the Node.js server. All files and folders should be in the app’s folder, not including public_html.
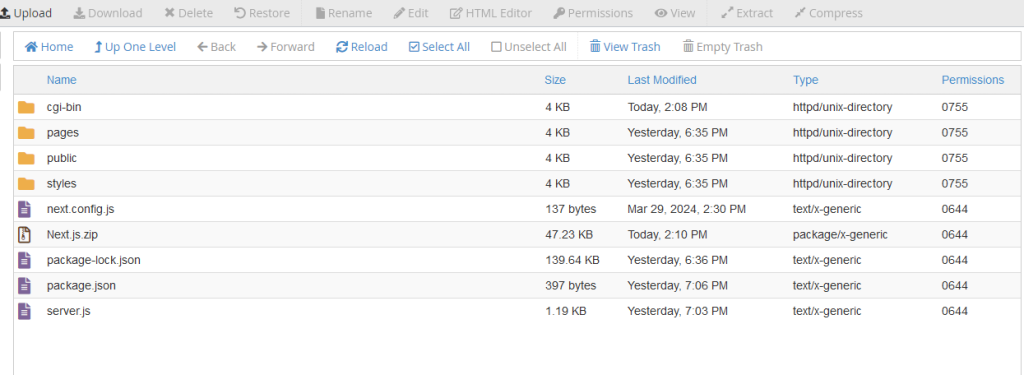
Below uploading files via File Manager:
Right-click on the uploaded file and choose Extract:
Log into your cPanel.
Navigate to File Manager.
Select or create a directory for your website content.
Select Upload in the top menu.
Choose the compressed file from your local machine and start the upload.
When the upload is complete, go back to the website directory.
6. Configure the Node.js app in cPanel
You can check how to work with Node.js app.
- In cPanel, find and open the Setup Node.js app.
- Select + CREATE APPLICATION.
- Configure the application settings:
Node.js version: select the version that matches the Node.js version you used when developing your app locally.
Application mode: select Production.
Application root: type the path of the directory where your website content is uploaded.
Application URL: select your domain name.
Application startup file: server.js.
If you have any environment variables, you can add them from your .env or .env.local file. For more information on environment variables in Next.js check Next.js Environment Variables Documentation. - Choose CREATE to create the Node.js application.
- Stop the app temporarily, then navigate to Detected Configuration Files.
- Select Run NPM Install to install Node.js packages.
- Start the app again by choosing START APP
Open a new tab in your web browser and enter your website URL. You should see your Next.js app running.
Congratulations! Your Next.js application should now be deployed on cPanel. Remember to check the application URL to ensure everything is working as expected. If you encounter any issues, check the error logs in cPanel or in your Next.js application.
We appreciate your feedback, questions, corrections, and any extra information related to this article. Please note that it might take some time for your comments to show up, and any off-topic comments will be removed.
If you need help with your account, don’t hesitate to reach out to our Support Team. Thank you!